OpenCasemix
The main objective of OpenCasemix is to show and explain on how to design a custom casemix system for your hospital need. I will also upload source code for the grouper and sample dataset to implement a working application. The code will be written in Python and the database is MySQL.
View coding section here
Definition
Casemix is a classification of patients treatment episodes designed to create classes which are relatively homogenous in respect of the resources used and contain patients with similar clinical characteristics; refers to the range and types of patients a hospital treats
(George Palmer, Beth Reid)
Casemix is a system that measures hospital performance, aiming to reward initiatives that increase efficiency in hospitals. It also serves as an information tool that allows policy makers to understand the nature and complexity of health care delivery.
(Wikipedia)
Business intelligence for healthcare.
(Me)
Modules
Casemix can be divided into two modules:
- Clinical Module [View code]
- Costing Module
Clinical Module
The clinical module is responsible for class assignment based on demographic and clinical inputs. The inputs are:
- Demographic data
- Age in days
- Gender
- Clinical data
- Length of Stay
- Principal diagnosis
- Principal procedure
- Morbidity/Mortality
Based on the inputs above, the ouput is a DRG group which will be assigned to the case.
The components of this module are:
- Major Diagnostic Criteria (MDC)
- Diagnosis Related Group (DRG)
- Severity of Illness (SOI)
- Clinical Codes (ICD10 & ICD9CM)
- Complication/Co-morbidity (CC) & Major Complication/Co-morbidity (MCC)
- Grouper (View code)
Pre-requisite:
- Casting of ICD codes to DRG classes
- Logic or decision tree
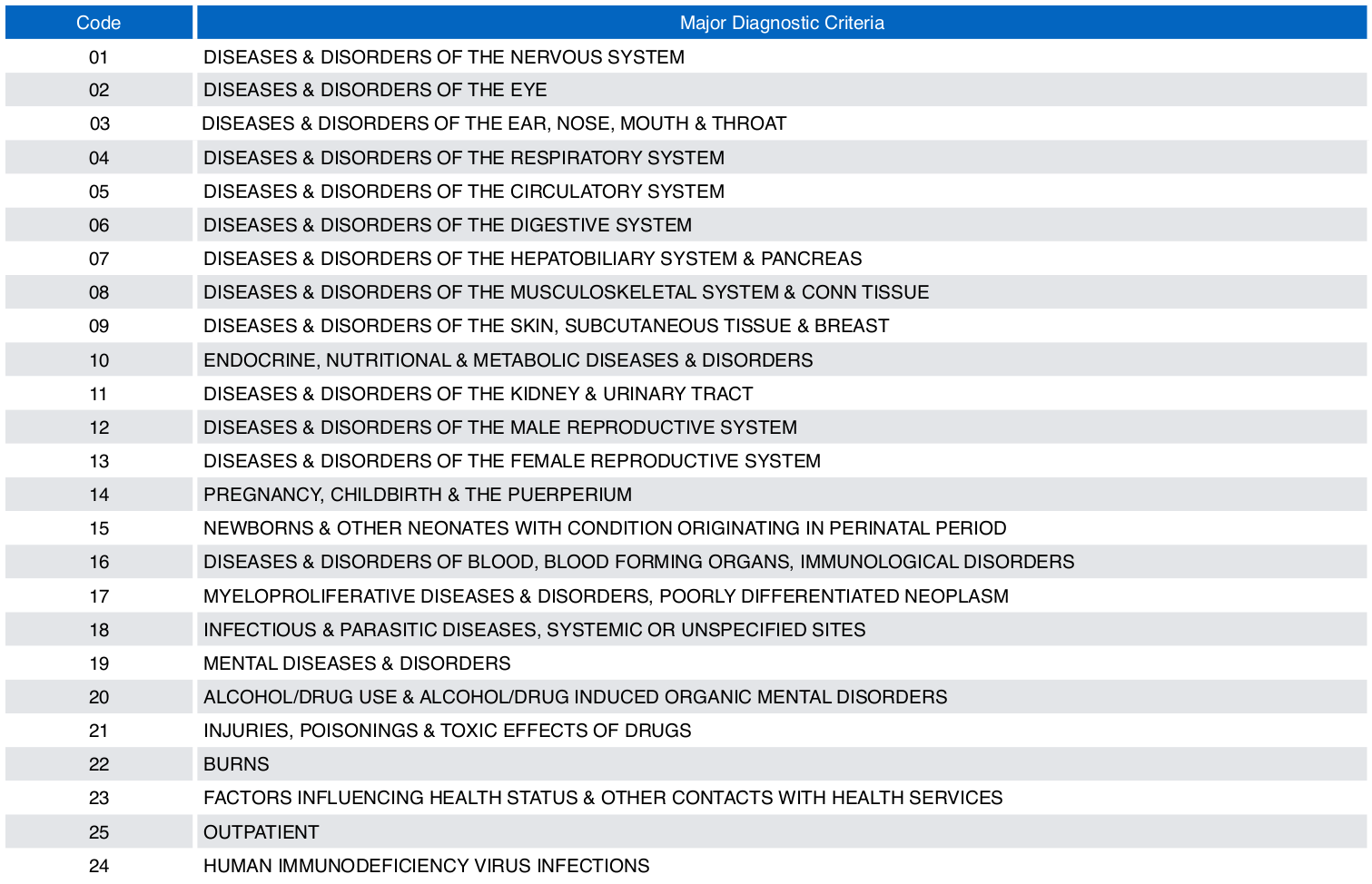
Major Diagnostic Criteria (MDC)
- MDC is the root classification
- There are 24 criterias
Diagnostic Related Group (DRG)
- Sub-class of MDC
- DRG can be further subdivided into:
- Medical
- Determined by principal diagnossis.
- Surgical
- Determined by principal procedure.
- Will overide medical DRG if a principal procedure is available.
- Medical
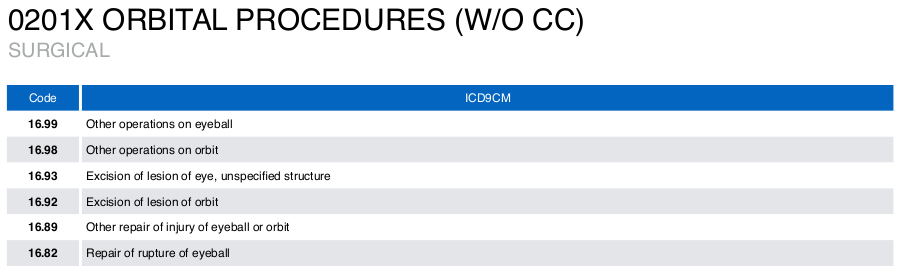
- Below is an example of a DRG list from MDC ‘02 Disease & Disorder of the Eye’
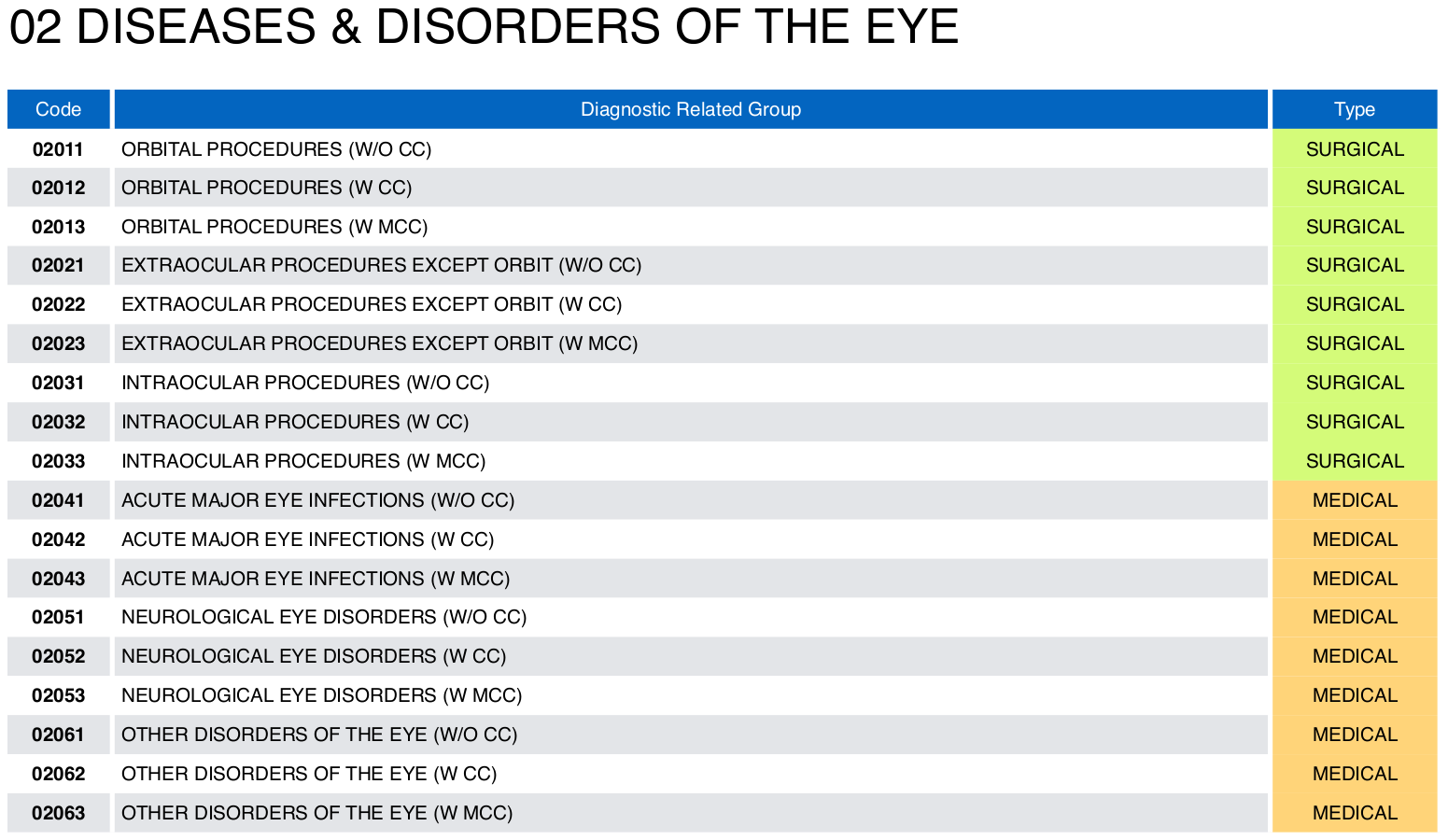
- The DRG code are divided into 3 sections as depicted by the image below:

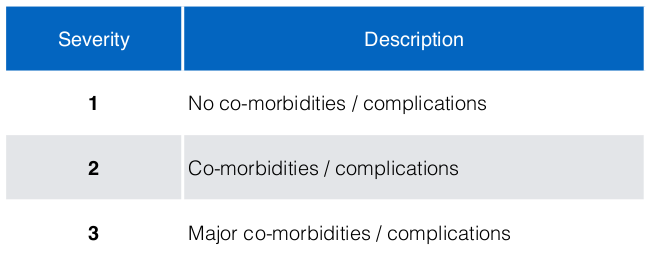
Severity of Illness (SOI)
Each DRG can be further classified into 3 severity of illness which is reflected by the last digit of each code. The level of severity is determined by the type co-morbidities or complications.
ICD10 & ICD9CM
DRG groups are made up of ICD10 and ICD9CM codes. These code will further classify each DRG into medical or surgical DRG. This casting process is not fixed and you can use modify or rearrange them according to your requirement.
- International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision
- International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification (Procedure Codes)
- You can download the ICD10 and ICD9CM code from my github page.
Medical DRG will consist of ICD10 codes. Example of a medical DRG:
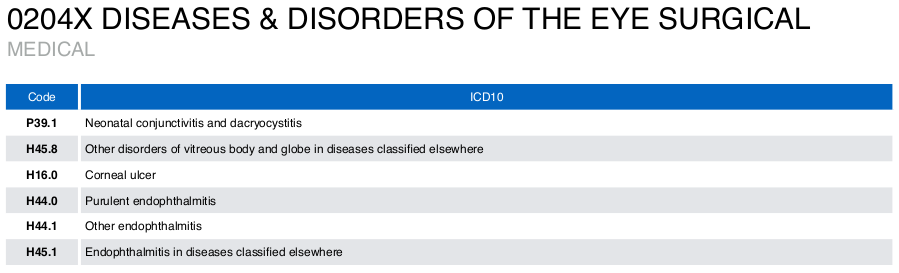
Surgical DRG will consist of ICD9CM codes. Example of a surgical DRG:
Complication/co-morbidity (CC) & Major complication/co-morbidity (MCC)
CC and MCC is a list of ICD10 codes grouped based on their severity and resource requirement. All ICD10 codes under CC is considered as SOI2 while MCC will be grouped as SOI3. While cases with secondary diagnosis or comorbidites where its ICD10 code is not listed under CC or MCC is SOI1.
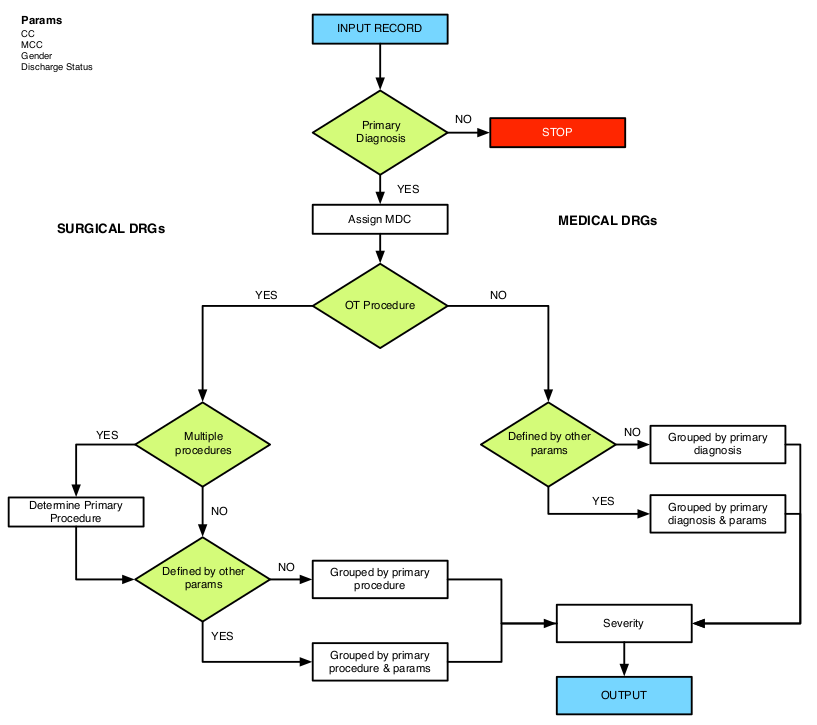
Grouper
This is an algorithm which takes clincal and demographic data as input and assign a corresponding DRG as an output. Below is an example of a decision tree for DRG assignment where the input is the clinical and demographic data and the output is DRG.
Costing Module
The costing module is mainly about the hospital financial information. Some variables in this section such as cost per bedday, cost per case (aka cost per discharge), direct cost or indirect cost can be gathered from the financial system. A top down costing is a commonly used method where the figures in each of the cost centers can be identified.
The objective of this module is to calculate the following:
- Cost per case
- Average cost per case
- Global average cost per case
- Case group weight (CGW)
- Hospital base rate
- Casemix index
Cost per case
Cost per case is the amount of cost to manage a case.
Average cost per case
The next step is to calculate the average cost per case. However outlier cases must first be discarded from the group. Outliers are cases where the length of stay differs significantly from others.
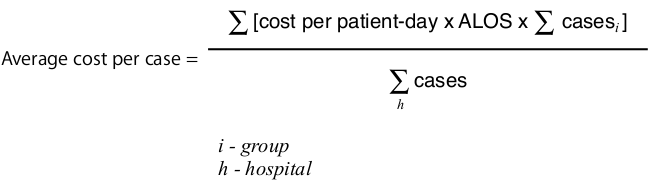
ALOS - Average length of stay
Global average cost per case
Global average cost per case can be derived from the weighted average of the cost per case in each case group.
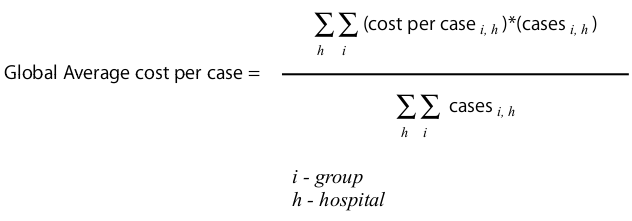
Case group weight (CGW)
In short it is the ratio of average cost per case against global average cost per case.
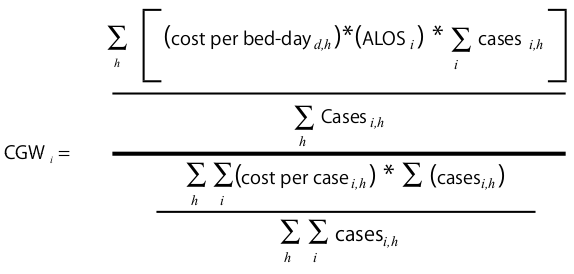
i - group
h - hospital
Hospital base rate
Hospital base rate is the sum of direct and indirect cost divided by the total number of the cases.
Casemix Index
Casemix index represents the resource intensity of cases treated in a hospital.
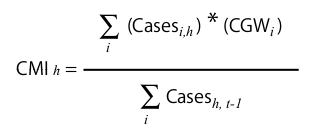
i - group
h - hospital
t-1 - previous year
I think there is enough information here to start coding. In the next update I will post codes on how to piece all the information above into a working casemix application.
View coding section here